Space Tech Revolution: NASA's Groundbreaking 3D-Printed Antenna Shatters Manufacturing Limits
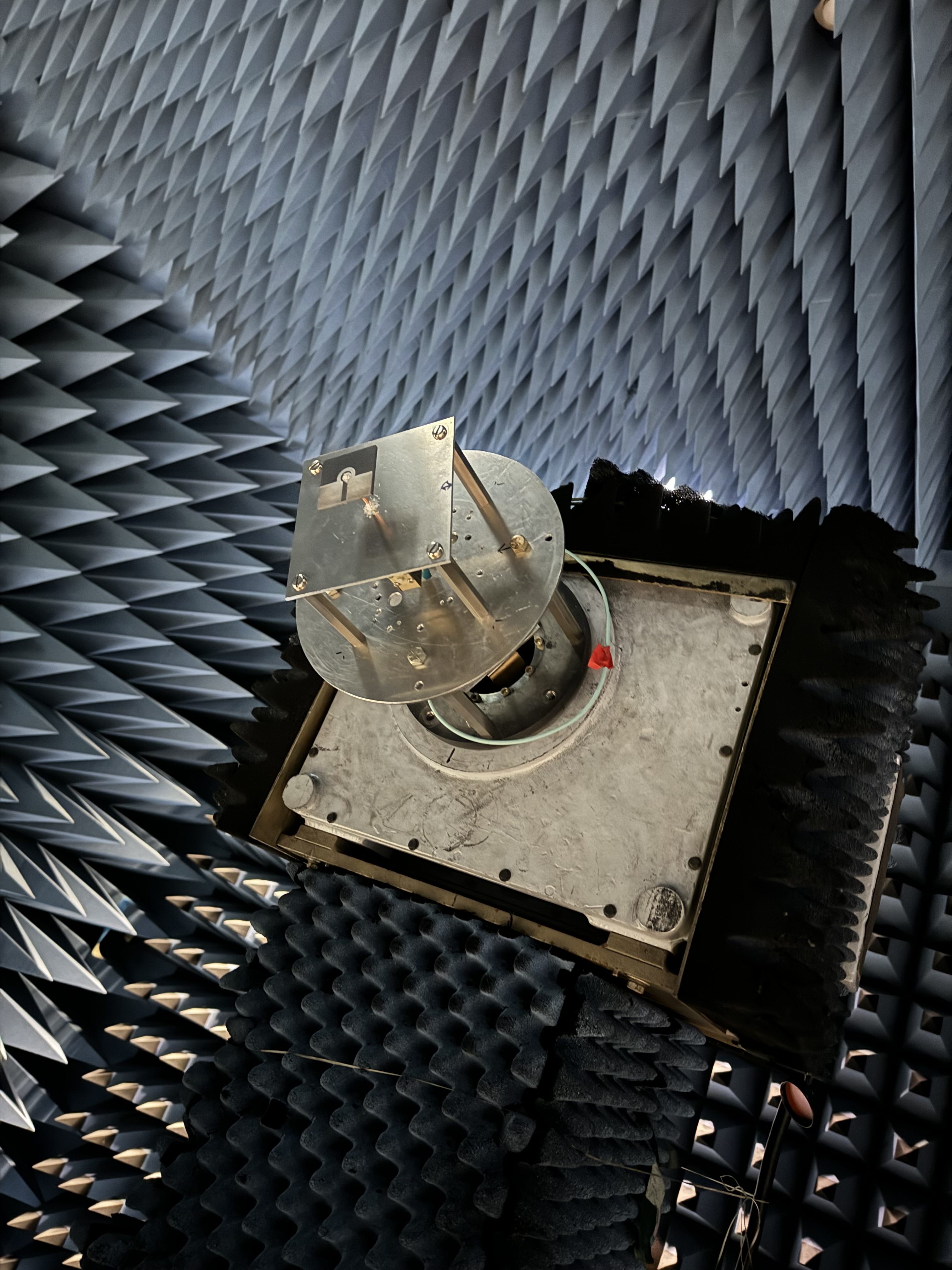
NASA Pioneers Innovative 3D-Printed Antenna Technology for Space Communications
In a groundbreaking advancement for space exploration, NASA has successfully developed and tested a cutting-edge 3D-printed antenna during the fall of 2024. This innovative technology represents a significant leap forward in reducing communication costs and enhancing data transmission capabilities from space missions.
The newly designed antenna showcases NASA's commitment to pushing the boundaries of space communication technology. By utilizing 3D printing techniques, the agency has demonstrated an affordable and efficient method for transmitting critical scientific data back to Earth. This breakthrough could potentially revolutionize how spacecraft and research missions share information across vast distances.
The test marks an important milestone in NASA's ongoing efforts to develop more cost-effective and adaptable communication solutions for future space exploration endeavors. By leveraging advanced manufacturing techniques like 3D printing, the agency continues to find creative ways to improve space technology while keeping mission expenses manageable.

